Carlos presented our recent results in charge transport, photoactivity and chemical reactivity in metal-organic frameworks at the ICIQ in the seminar programme sponsored by BASF.. Thanks for the invitation Mónica and JR! See here for more info.
Our Funimates Isabel, Jose and Javi attended the EuroMOF2019 conference held in Paris to present and discuss our latest advances in Titanium-Organic frameworks and enzyme encapsulation in MOFs. More info.
Carmen, María, Belén, Javi and Isabel attended the last XVI Simposio de Jóvenes Investigadores de la Real Sociedad Española de Química which took place in the Universitat Politècnica of Valencia. They had the opportunity to present their recent results and interact with Spanish young researchers. More info here.
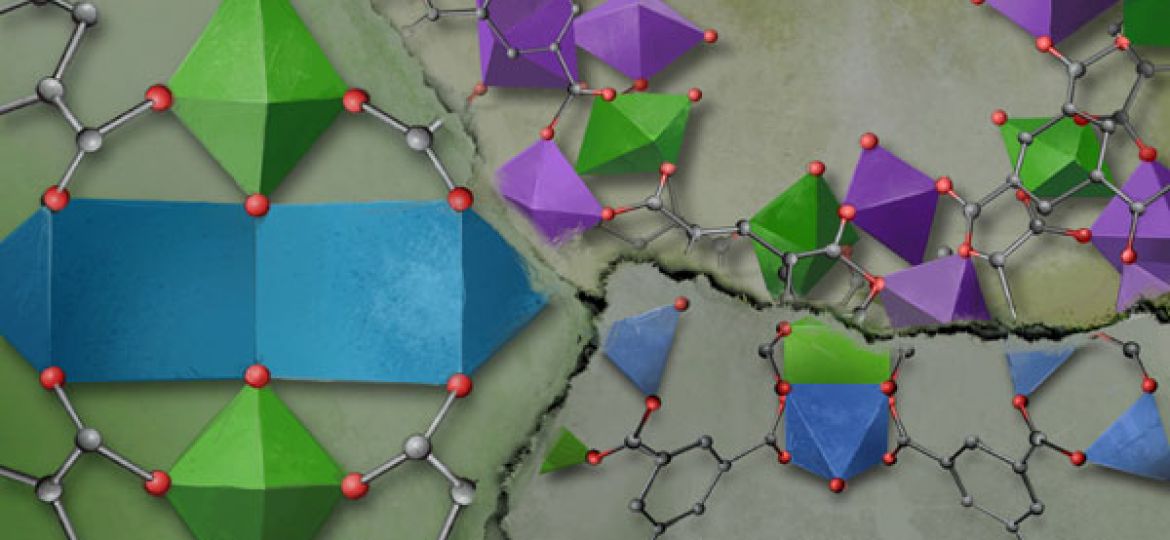
Natalia and Belens work has been published in JACS. Their work introduces a pioneering methodology for the synthesis of heterometallic titanium frameworks amenable to the principles of reticular chemistry. Instead of relying in the serendipitous discovery of mixed-metal clusters by trial and error, we use heterometallic MOF crystals as precursors to direct the formation of SBUs with variable connection points by metal exchange reactions at low temperature. Click for more info
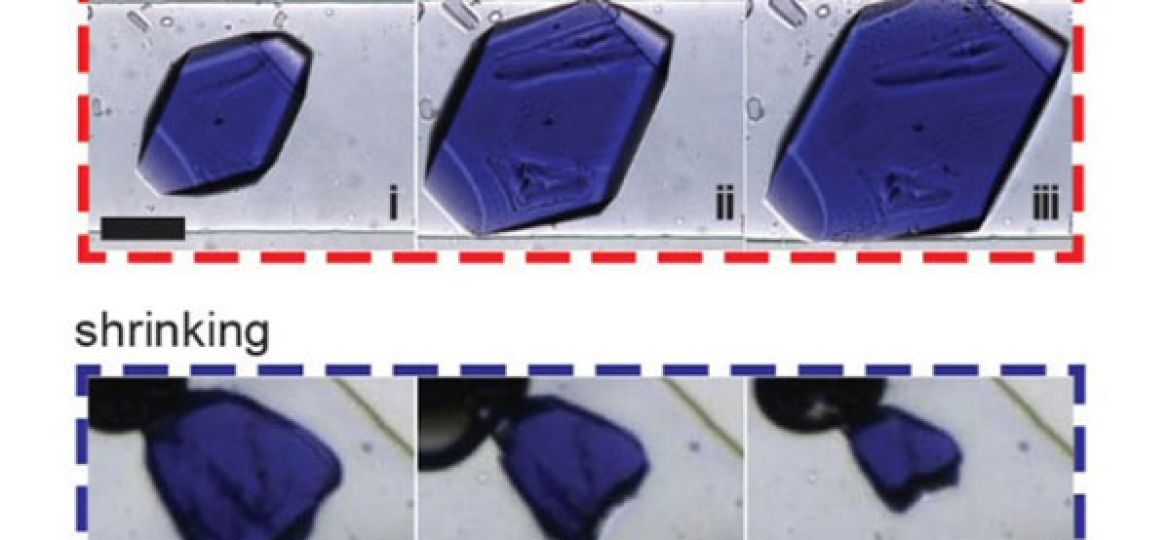
We are really happy to see our collaboration with Puigmartí-Luis group published in JACS. By using microfluidic chips we manage to grow and shape crystals of our beloved Cu(GHG) peptide MOF at the millimeter scale. This approach permits generating monolith single crystals and might help overcoming the problems associated with the pelletization and densification of these materials for their successful implementation into functional devices. Click for more info
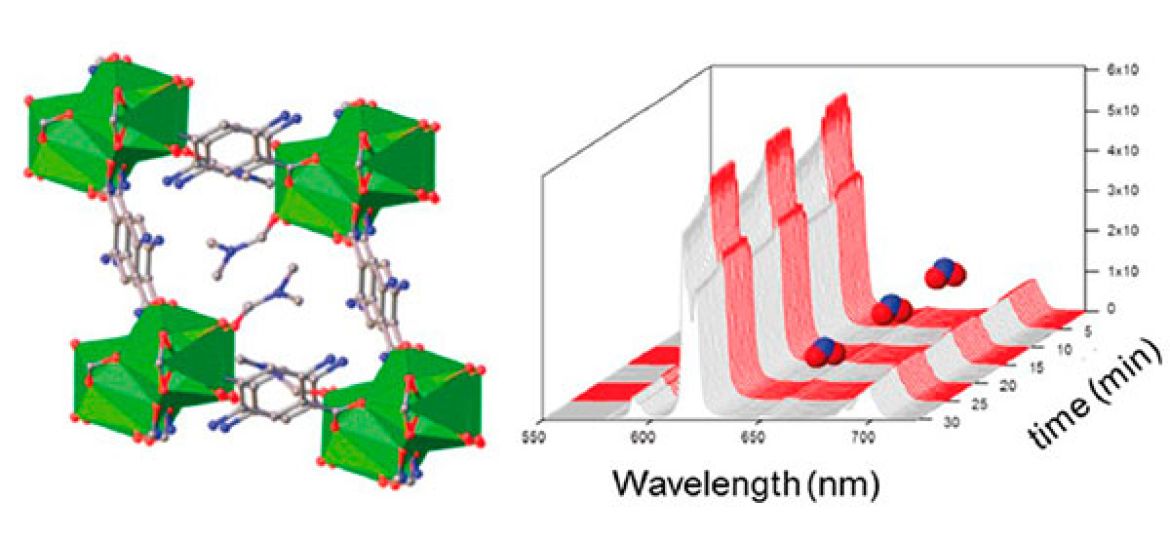
Our collaboration with Sánchez-Costa lab at IMDEA has been published in the cover of the Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters. This work introduces a new sensing mechanism controlled by the interaction of NOx contaminants with the framework for concomitant increase/decrease in the luminescence of the solid. Click for more info
Carlos was invited to present our recent results of relevance in biotechnological applications at the annual meeting of Biotecmed, to celebrate its recent certification as scientific institute of the Universidad de Valencia. We are excited to push hard our ongoing collaborations with our biological colleagues!
Funimat was present at the ACS Symposium held in San Diego. Carlos and Sergio presented our recent results in photoactive titanium frameworks and charge transport in ultrathin films in the MOF symposium.
Francisco G. Cirujano was present at the award ceremony of La Caixa research fellowships, awarded for the development of new methodologies for the efficient synthesis of pharmaceuticals. For more details see here.
Our work on the synthesis of hydroxamic titanium frameworks has been highlighted as supplementary cover in JACS. Thanks to the creative team of Principia for the excellent result. Hope you will like it!